Understanding Human Behaviour Without Spoken Words

Edwin Ogie Library is a dynamic platform for education, focused on fostering mindful communication and building positive relationships by eliminating linguistic errors. Our mission is to enhance connections through thoughtful language, emotional regulation, and self-awareness, providing educational resources that inspire personal growth. We aim to promote well-being, peace, and meaningful connections, offering a space for individuals committed to refining their communication skills.

iturn0image0turn0image1turn0image4turn0image6Waves exhibit several fundamental behaviors as they interact with different media and obstacles. The primary properties of waves include reflection, refraction, diffraction, interference, and polarization. Understanding these properties is crucial in fields ranging from optics and acoustics to quantum mechanics.
1. Reflection
Reflection occurs when a wave encounters a boundary or obstacle and bounces back into the original medium. The angle at which the wave strikes the surface (angle of incidence) is equal to the angle at which it reflects (angle of reflection). This principle is observed in both mechanical waves, like sound, and electromagnetic waves, such as light.
Illustration:
Example: An echo is a result of sound waves reflecting off a distant surface and returning to the listener.
2. Refraction
Refraction is the bending of a wave as it passes from one medium into another with a different density, resulting in a change in the wave's speed and direction. This phenomenon is responsible for effects like the apparent bending of a straw in a glass of water.
Illustration:

Example: Light waves refract when transitioning from air into water, causing objects submerged in water to appear shifted from their actual positions.
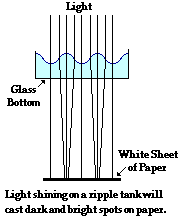
3. Diffraction
Diffraction involves the spreading out of waves as they pass through a narrow opening or around obstacles. The extent of diffraction depends on the relationship between the wavelength of the wave and the size of the opening or obstacle.
Illustration:

Example: The ability to hear someone speaking even when they are around a corner is due to the diffraction of sound waves bending around obstacles.
4. Interference
Interference occurs when two or more waves overlap in space, leading to a new wave pattern. This can result in constructive interference, where wave amplitudes add together, or destructive interference, where they cancel each other out.
Illustration:

Example: The colorful patterns seen in soap bubbles are due to the interference of light waves reflecting off the different layers of the bubble's surface.
5. Polarization
Polarization is a property specific to transverse waves, such as light, where the oscillations occur in particular orientations. By filtering these orientations, it's possible to block certain wave vibrations, a principle utilized in polarized sunglasses to reduce glare.
Illustration:

Example: Polarized sunglasses reduce glare by blocking horizontally polarized light reflected from surfaces like water or roads.
Comments
Post a Comment
We’d love to hear from you! Share your thoughts or questions below. Please keep comments positive and meaningful, Comments are welcome — we moderate for spam and civility; please be respectful.